AI-driven learning in physical education: A bibliometric analysis of trends, knowledge structure, and future research directions
Downloads
Background: Although research on AI-driven learning in PE has expanded rapidly, existing studies remain fragmented across disciplines, journals, and methodological approaches, limiting a comprehensive understanding of the field's development and intellectual structure.
Objectives: This study aimed to systematically map the evolution, influential contributors, intellectual structure, dominant themes, and future research directions of AI-driven learning research in physical education from a bibliometric perspective.
Methods: A quantitative bibliometric analysis was conducted using data retrieved exclusively from the Scopus database. A total of 284 eligible documents published between 2020 and early 2026 were analyzed. Descriptive statistics were applied to examine publication trends, authorship, sources, institutions, and country contributions. Network and thematic analyses were performed using VOSviewer (version 1.6.20) and the Bibliometrix package in R to identify co-authorship patterns, keyword co-occurrence networks, and thematic clusters.
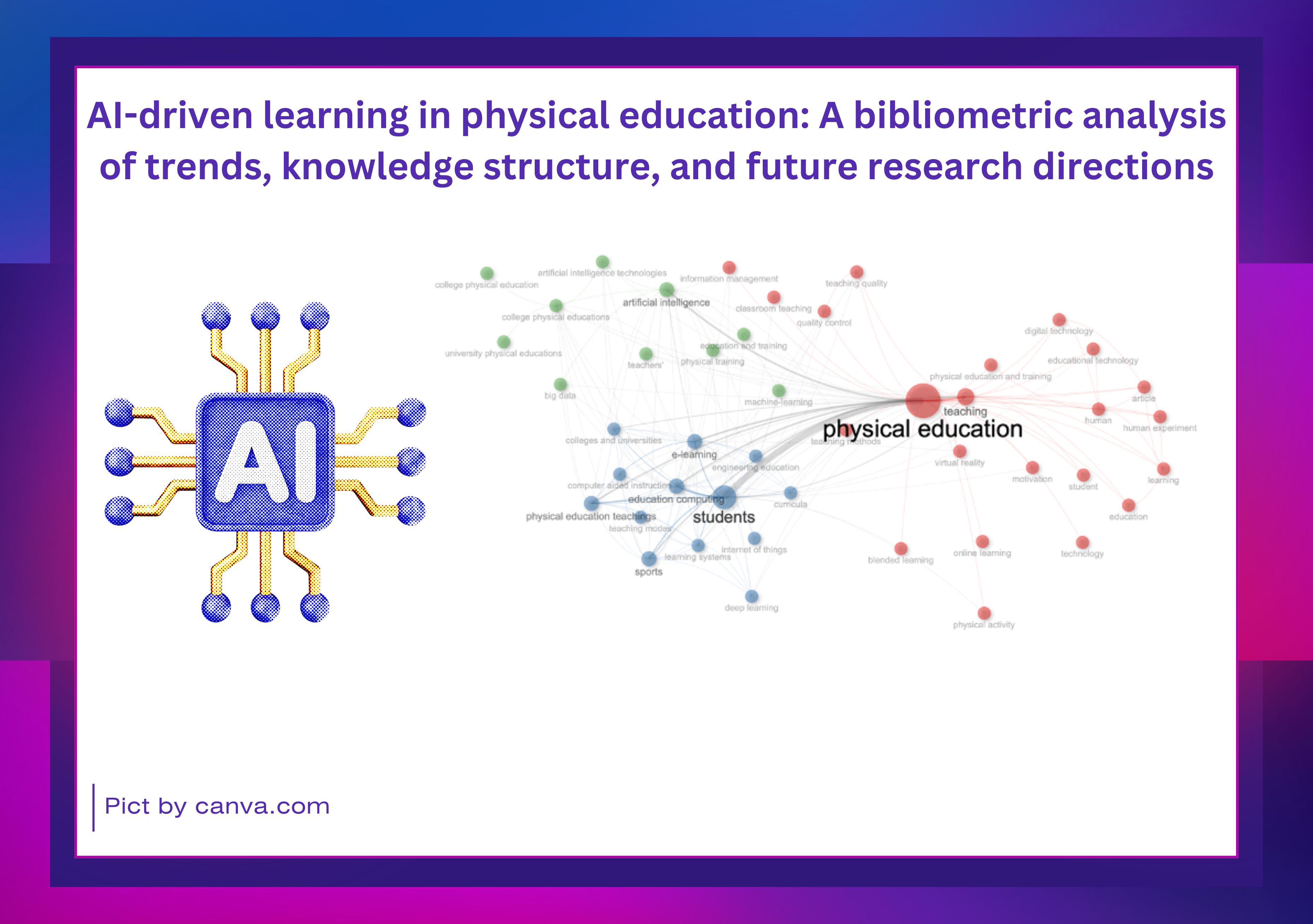
Results: The results indicate a sharp growth in AI-driven learning research in physical education after 2022, with publication output increasing more than fivefold from 2020 to 2025. China emerged as the leading contributing country, accounting for nearly half of the total publications, while institutional productivity was concentrated in several Russian universities. Keyword co-occurrence analysis revealed five major thematic clusters shaping the intellectual structure of the field, integrating pedagogical frameworks, computational intelligence, institutional contexts, and physical training models. Dominant research themes centered on pedagogical design, student engagement, adaptive learning systems, and the integration of educational technology. Emerging themes included virtual reality, advanced machine learning techniques, and immersive learning environments.
Conclusions: This study provides a structured and quantitative overview of AI-driven learning research in physical education, highlighting its interdisciplinary nature and rapid expansion.Calderón, A., Meroño, L., & MacPhail, A. (2020). A student-centred digital technology approach: The relationship between intrinsic motivation, learning climate and academic achievement of physical education pre-service teachers. European Physical Education Review, 26(1), 241–262. https://doi.org/10.1177/1356336X19850852
Chang, K. E., Zhang, J., Huang, Y. S., Liu, T. C., & Sung, Y. T. (2020). Applying augmented reality in physical education on motor skills learning. Interactive Learning Environments, 28(6), 685-697. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2019.1636073
Chen, J., & Zeng, B. (2022). Development Trend of Digital Physical Education Teaching by Integrating Intelligent Sensor Technology. Security and Communication Networks, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3039349
Cheng, G. (2024). Analysis of the psychological and physiological conditions of blockchain technology in college physical education. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.2478/amns-2024-0831
Deng, X., Bai, X., & Li, Z. (2024). Challenges and applications of multi-model learning analytics in decision support for physical education teaching in the context of intuitionistic fuzzy Z-numbers. Journal of Computational Methods in Sciences and Engineering, 14727978251364132. https://doi.org/10.1177/14727978251364132
Gil-Espinosa, F. J., Nielsen-Rodríguez, A., Romance, R., & Burgueno, R. (2022). Smartphone applications for physical activity promotion from physical education. Education and Information Technologies, 27(8), 11759–11779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11108-2
Guo, Q., & Li, B. (2021). Role of AI physical education based on application of functional sports training. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems, 40(2), 3337–3345. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-189373
Krause, J. M., O’Neil, K., & Jones, E. M. (2020). Technology in Physical Education Teacher Education: A Call to Action. Quest, 72(3), 241–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/00336297.2019.1685553
Lee, H. S., & Lee, J. (2021). Applying artificial intelligence in physical education and future perspectives. Sustainability (Switzerland), 13(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010351
Lee, J. E., & Gao, Z. (2020). Effects of the iPad and mobile application-integrated physical education on children’s physical activity and psychosocial beliefs. Physical Education and Sport Pedagogy, 25(6), 567–584. https://doi.org/10.1080/17408989.2020.1761953
Li, X., Tan, W. H., Zheng, X., Dou, D., Wang, Y., & Yang, H. (2025). Effects of digital monitoring and immediate feedback on physical activity and fitness in undergraduates. Education and Information Technologies, 30(3), 3743–3769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12990-8
Lindberg, R., Seo, J., & Laine, T. H. (2016). Enhancing physical education with exergames and wearable technology. IEEE transactions on learning technologies, 9(4), 328-341. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2016.2556671
Mason, A. J., & Kulinna, P. H. (2022). Digital Projection for Teaching and Learning in Physical Education. Journal of Physical Education, Recreation and Dance, 93(8), 22–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/07303084.2022.2108172
Meng, J. (2021). College physical education teaching aided by virtual reality technology. Mobile Information Systems, 2021(1), 3052895. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3052895
Mokmin, N. A. M. (2020). The effectiveness of a personalized virtual fitness trainer in teaching physical education by applying the artificial intelligent algorithm. International Journal of Human Movement and Sports Sciences, 8(5), 258–264. https://doi.org/10.13189/saj.2020.080514
Pill, S., SueSee, B., Hyndman, B., & Williams, J. (2021). Physical education teachers’ use of digital game design principles. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 40(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1123/JTPE.2019-0036
Pratama, B. A., Sucipto, S., & Hanief, Y. N. (2022). Improving learning in physical education: Augmented reality mobile app-based for fundamental motor skill. Jurnal SPORTIF: Jurnal Penelitian Pembelajaran, 8(2), 314-326. https://doi.org/10.29407/js_unpgri.v8i2.18508
Sargent, J., & Casey, A. (2021). Appreciative inquiry for physical education and sport pedagogy research: a methodological illustration through teachers’ uses of digital technology. Sport, Education and Society, 26(1), 45–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/13573322.2019.1689942
Sargent, J., & Lynch, S. (2021). ‘None of my other teachers know my face/emotions/thoughts’: digital technology and democratic assessment practices in higher education physical education. Technology, Pedagogy and Education, 30(5), 693–705. https://doi.org/10.1080/1475939X.2021.1942972
Vega, L., Notario, R. O., & Ávalos-Ramos, M. A. (2020). The relevance of mobile applications in the learning of physical education. Education Sciences, 10(11), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10110329
Xu, J., & Wang, D. (2022). Design of Comprehensive Rating Algorithm for Classroom Teaching Effect under the Background of Sports Education Integration. Mobile Information Systems, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1228198
Xu, Y., Huang, S., & Li, L. (2022). Quality Evaluation and Informatization Analysis of Physical Education Teaching Reform Based on Artificial Intelligence. Security and Communication Networks, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5473153
Yang, D., Oh, E.-S., & Wang, Y. (2020). Hybrid physical education teaching and curriculum design based on a voice interactive artificial intelligence educational robot. Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(19), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198000
Yang, H., Huang, B., & Li, X. (2025). Augmentation or substitution: defining role of large language model in physical education. Frontiers in Sports and Active Living, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fspor.2025.1662056
Yang, P., & Qian, S. (2025). The Factors Affecting Students’ Behavioral Intentions to Use E-learning for Educational Purposes: A Study of Physical Education Students in China. SAGE Open, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440251313654
Yang, S. (2024). Innovation of Physical Education and Health Curriculum Teaching Models in Colleges and Universities in the Digital Era and Its Contribution to Students’ Core Literacy. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.2478/amns-2024-3256
Zhang, J. (2025). Leveraging Artificial Intelligence for Enhanced Physical Education in Universities: A Paradigm Shift Towards Data-Driven and Adaptive Learning Systems. International Journal of Web-Based Learning and Teaching Technologies, 20(1). https://doi.org/10.4018/IJWLTT.393622
Zhang, R. (2024). Construction and Evaluation of Digital Resource Management Platform for Physical Education in Colleges and Universities. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.2478/amns-2024-3272
Copyright (c) 2026 Amelia Larassary

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.